Can I Get Social Security Disability Benefits for Asthma?
- How Does the Social Security Administration Decide if I Qualify for Disability Benefits for Asthma?
- About Asthma and Disability
- Winning Social Security Disability Benefits for Asthma by Meeting a Listing
- Residual Functional Capacity Assessment for Asthma
- Getting Your Doctor’s Medical Opinion About What You Can Still Do
How Does the Social Security Administration Decide if I Qualify for Disability Benefits for Asthma?
If you have asthma, Social Security disability benefits may be available. To determine whether you are disabled by asthma, the Social Security Administration first considers whether your asthma is severe enough to meet or equal a listing at Step 3 of the Sequential Evaluation Process. See Winning Social Security Disability Benefits for Asthma by Meeting a Listing. If you meet or equal a listing because of asthma, you are considered disabled. If your asthma is not severe enough to equal or meet a listing, Social Security Administration must assess your residual functional capacity (RFC) (the work you can still do, despite your asthma), to determine whether you qualify for benefits at Step 4 and Step 5 of the Sequential Evaluation Process. See Residual Functional Capacity Assessment for Asthma.
About Asthma and Disability
Asthma is a type of chronic obstructive lung disease (COPD). It is a chronic inflammatory disease of the breathing or bronchial tubes (see Figure 1 below). Muscles in the bronchial tubes constrict due to irritation, which can be an innate problem or can be caused by inhaling certain substances. In addition to constriction, inflammation causes swelling and excess mucus that further narrows the bronchial tubes. The combination of constricting muscles and inflammation obstructs the flow of air in the lungs. Asthmatic attacks can cause shortness of breath, chest tightness, wheezing, and coughing.
Asthma can also be called asthmatic bronchitis, chronic asthmatic bronchitis, or reactive airways disease. Asthma frequently begins in childhood or adolescence, but can occur at any time in adult life.
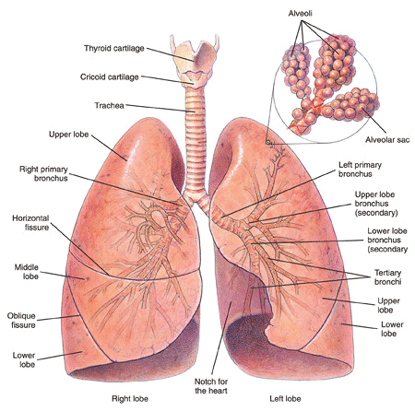
Figure 1: Diagram of the bronchial tubes and lungs.
Severity of Asthma Attacks
Asthma attacks can be mild and infrequent, responding to an inhaled bronchodilator. They can also be frequent and severe enough to be life-threatening. A diagnosis of asthma alone does not mean you are entitled to Social Security disability benefits. When properly treated, people with asthma have participated in the Olympics, professional sports, amateur sports, and school-related sports without danger or difficulty.
Treatment for Asthma
For years researchers have studied genetic, environmental, and immunological factors that may play a role in asthma. Despite gaps in knowledge, they have made considerable progress in treatment. Both the inflammation and the bronchial narrowing must be controlled for effective treatment. Patients with chronic asthma who receive inhaled steroids to reduce inflammation along with bronchodilators to relax tight muscles do better than those who receive bronchodilators alone. Many asthma patients do not receive the proper type or optimum dose of medications. Also, some asthma patients continue to smoke cigarettes, and others cannot or will not follow prescribed therapy.
Asthma Attack Triggers
Asthma is worsened by the air pollution common in larger cities. Intense emotion, cold air, dusts, pollens, and other types of air particulates can bring on an attack. Asthma attacks can be related to exposure to various pollutant or industrial gases, particularly sulfur dioxide (SO2) and nitric oxide (NO2). Respiratory viral infections can make bronchial inflammation worse and can precipitate asthmatic attacks. Allergic rhinitis (“hay fever”) and sinusitis are associated with worse asthmatic symptoms. Some medications tend to increase bronchial mucous secretion and bronchial constriction and can worsen symptoms. Heartburn can worsen bronchial irritation if stomach acid is inhaled into the airway. So multiple medical and environmental factors must be evaluated and controlled for the best therapeutic results. See Asthma Triggers in the Workplace.
Related Conditions
Individuals with asthma can also have other types of obstructive or restrictive lung disease, which can complicate diagnosis, treatment, and the Social Security disability determination. Smokers with emphysema and chronic bronchitis have inflammation of their airways that results in broncho-constriction, although they would not be considered to have true asthma. They may be treated with bronchodilator drugs, such as theophylline, if the constriction is reversible. But be aware that the Social Security Administration will not assume that you have a particular condition just because you take a particular medication.
Winning Social Security Disability Benefits for Asthma by Meeting a Listing
To determine whether you are disabled at Step 3 of the Sequential Evaluation Process, the Social Security Administration will consider whether your asthma is severe enough to meet or equal the asthma listing. The Social Security Administration has developed rules called Listing of Impairments for most common impairments. The listing for a particular impairment describes a degree of severity that the Social Security Administration presumes would prevent a person from performing substantial work. If your asthma is severe enough to meet or equal the asthma listing, you will be considered disabled.
The listing for asthma is 3.03, which has two parts: A and B. You will be eligible for Social Security disability benefits if you meet either part.
Meeting Social Security Administration Listing 3.03A for Asthma
According to this listing, if you are diagnosed with chronic asthmatic bronchitis, you will be evaluated under the criteria for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in listing 3.02A (Chronic Pulmonary Insufficiency), which provides that a claimant is disabled if he or she has:
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease due to any cause, with the FEV1 equal to or less than the values specified in Table I corresponding to the person’s height without shoes.
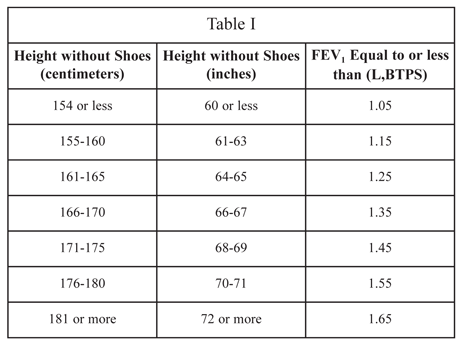
FEV1 is measured by a spirometer. The device measures the volume of air that you can inhale and exhale and displays the result on a graph called a spirogram. Spirometry is the most important test for evaluating obstructive lung disease. FEV1, which stands for forced expiratory volume in one second, decreases in proportion to the severity of the lung disease. In other words, the lower your FEV1, the more severe your lung disease is.
Meeting Social Security Administration Listing 3.03B for Asthma
A Social Security disability claimant with asthma meets listing 3.03(B) and is disabled if he or she has:
Attacks in spite of prescribed treatment and requiring physician intervention, occurring at least once every 2 months or at least six times a year. Each in-patient hospitalization for longer than 24 hours for control of asthma counts as two attacks, and an evaluation period of at least 12 consecutive months must be used to determine the frequency of attacks.
Attacks of asthma are defined as:
Prolonged symptomatic episodes lasting one or more days and requiring intensive treatment, such as intravenous bronchodilator or antibiotic administration or prolonged inhalational bronchodilator therapy in a hospital, emergency room or equivalent setting.
Therefore, not every asthma attack counts. To meet Listing 3.03B, you must have attacks that require a trip to the ER or treatment by a doctor to control. Attacks that you can control yourself with your inhaler or home nebulizer do not count.
Documentation of your medical treatment is the key to winning a disability claim under listing 3.03B. Note the phrase “in spite of prescribed treatment…” If you don’t have a medical history, you cannot possibly qualify under part B since you cannot satisfy the requirement of being under the care of a physician.
Continue to Residual Functional Capacity Assessment for Asthma.




